TECHNOLOGY

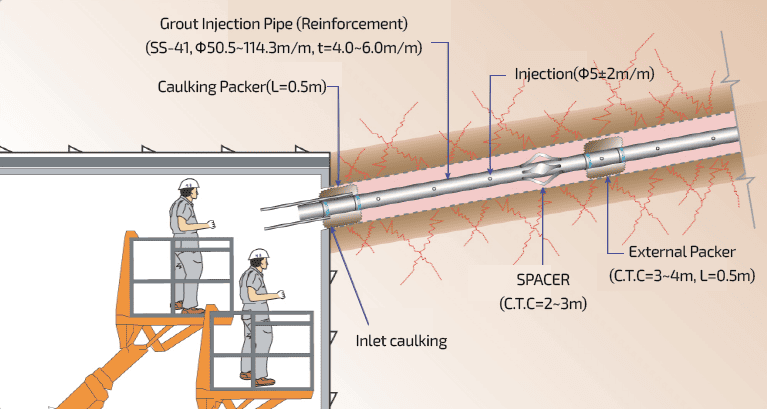
Continuous Steel Pipe Reinforcement Grouting Methods
Continuous Steel Reinforcement Grouting Process Overview
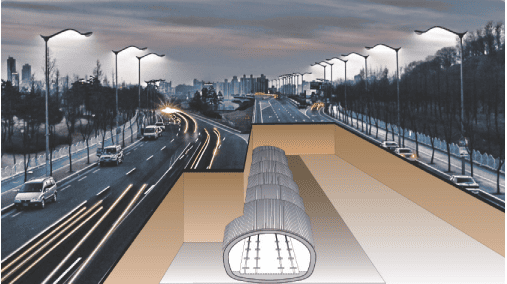
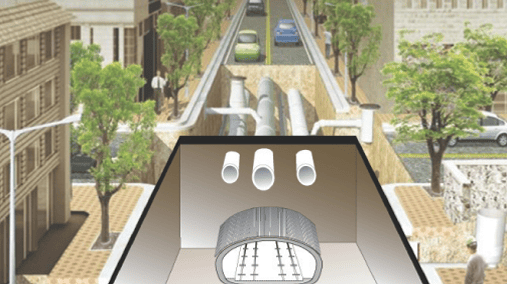
A method of increasing the strength of the original ground, blocking the inflow of groundwater,
and distributing and reducing the dead load and earth pressure on the tunnel
by installing processed steel pipes in an appropriate shape before tunnel excavation and injecting grout
into the surrounding ground in multiple stages using continuous packers on the inside of the steel pipes.
and distributing and reducing the dead load and earth pressure on the tunnel
by installing processed steel pipes in an appropriate shape before tunnel excavation and injecting grout
into the surrounding ground in multiple stages using continuous packers on the inside of the steel pipes.
1
Structural and Compensatory Safeguards
2
Apply Effects
- •
Geotechnical reinforcement and differential effects of injectables
- •
Beam Arching Effect by Reinforcement (Steel Pipe)
- •
Topsoil pressure relief
- •
Reduced relaxation zone
- •
Preventing surface subsidence and heave
- •
Displacement suppression effect on sidewalls
3
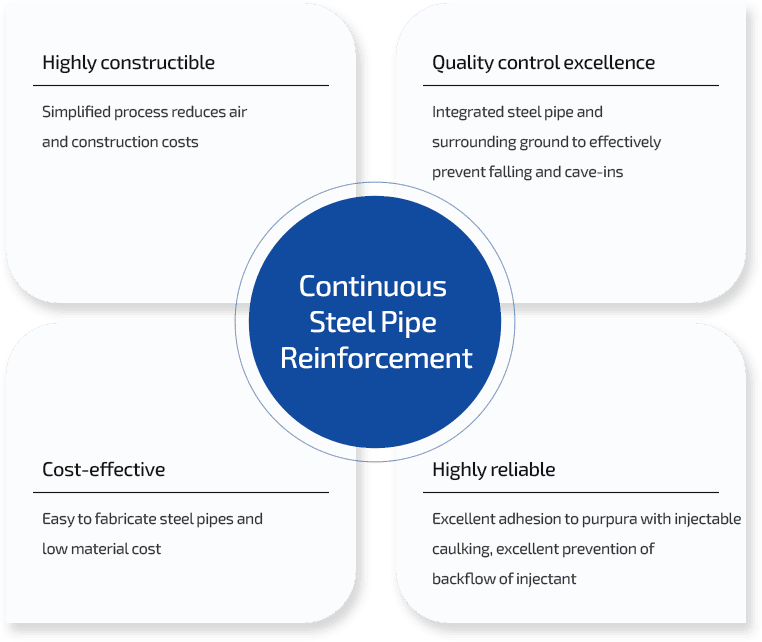
Excellence in construction
4
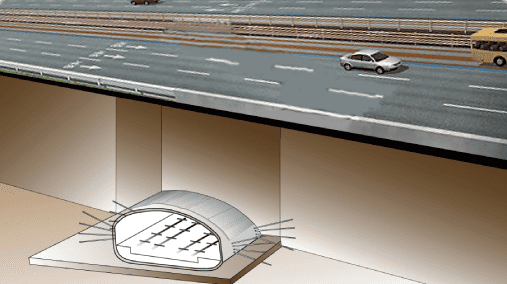
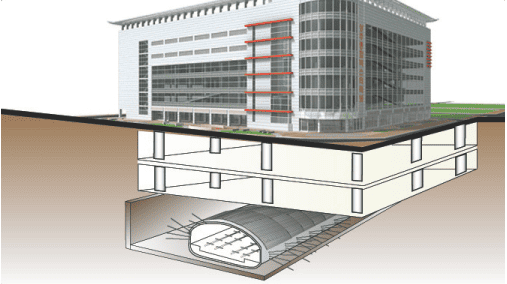
Coverage
5
Method Features
| How to apply traditional methods | How the patent method works | |
|---|---|---|
| Method Features |
How we staff
|
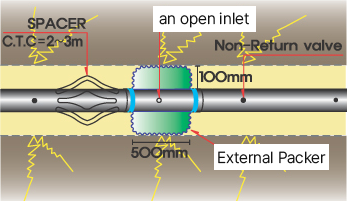
Adopt packer-based injection
|
 |
 |
|
| Sealing |
Separate pouring before grouting
|
Co-Injection with External Packers
|
 |
 |
|
| Spacers |
Attaching Spacers to Steel Pipe
|
|
 |
 |
|
| Non-Return Valves |
Rubber banding the injection holes
|
Installing an Injection Hole Non-Return Valve
|


 ENG
ENG KOR
KOR